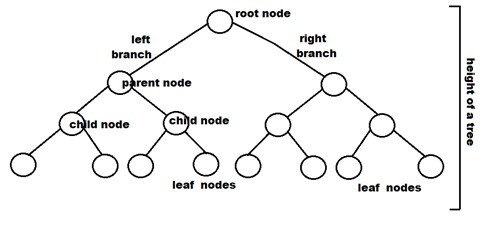
A tree is a data structure that consists of nodes in a parent/child relationship. It starts with a root node and every node has a value and a list of children nodes. The root node is the only node that doesn't have a parent. A leaf node is a node that doesn't have any children.
A binary tree is a tree in which each node has up to two children, referred to as the left child and the right child.
There are three main ways to traverse a binary tree:
- In-order: In-order traversal visits the left branch, then the current node, and finally the right branch.
- Pre-order: Pre-order traversal visits the current node before its children.
- Post-order: Post-order traversal visits the current node after its children.
1. Traverse the left subtree.
2. Visit the root.
3. Traverse the right subtree.
1. Visit the root.
2. Traverse the left subtree.
3. Traverse the right subtree.
1. Traverse the left subtree.
2. Traverse the right subtree.
3. Visit the root.
1. Create a new node.
2. Starting at the root:
a. Check if there is a root, if not, the new node becomes the root.
b. If there is a root, check if the value of the new node is greater than or less than the value of the root.
c. If it is greater:
i. Check to see if there is a node to the right.
ii. If there is, move to that node and repeat these steps.
iii. If there is not, add that node as the right property.
d. If it is less:
i. Check to see if there is a node to the left.
ii. If there is, move to that node and repeat these steps.
iii. If there is not, add that node as the left property.
1. Starting at the root:
a. Check if there is a root, if not, the tree is empty.
b. If there is a root, check if the value of the new node is greater than or less than the value of the root.
c. If it is greater:
i. Check to see if there is a node to the right.
ii. If there is, move to that node and repeat these steps.
iii. If there is not, the node does not exist in the tree.
d. If it is less:
i. Check to see if there is a node to the left.
ii. If there is, move to that node and repeat these steps.
iii. If there is not, the node does not exist in the tree.
A binary search tree is a binary tree in which every node has no more than two children. The left child is always less than the parent node, and the right child is always greater than the parent node.
1. Create a new node.
2. Starting at the root:
a. Check if there is a root, if not, the new node becomes the root.
b. If there is a root, check if the value of the new node is greater than or less than the value of the root.
c. If it is greater:
i. Check to see if there is a node to the right.
ii. If there is, move to that node and repeat these steps.
iii. If there is not, add that node as the right property.
d. If it is less:
i. Check to see if there is a node to the left.
ii. If there is, move to that node and repeat these steps.
iii. If there is not, add that node as the left property.
1. Starting at the root:
a. Check if there is a root, if not, the tree is empty.
b. If there is a root, check if the value of the new node is greater than or less than the value of the root.
c. If it is greater:
i. Check to see if there is a node to the right.
ii. If there is, move to that node and repeat these steps.
iii. If there is not, the node does not exist in the tree.
d. If it is less:
i. Check to see if there is a node to the left.
ii. If there is, move to that node and repeat these steps.
iii. If there is not, the node does not exist in the tree.
1. Starting at the root:
a. Check if there is a root, if not, the tree is empty.
b. If there is a root, check if the value of the new node is greater than or less than the value of the root.
c. If it is greater:
i. Check to see if there is a node to the right.
ii. If there is, move to that node and repeat these steps.
iii. If there is not, the node does not exist in the tree.
d. If it is less:
i. Check to see if there is a node to the left.
ii. If there is, move to that node and repeat these steps.
iii. If there is not, the node does not exist in the tree.
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. It maintains the property that the height of the left and right subtrees of every node differs by at most one.
1. Create a new node.
2. Starting at the root:
a. Check if there is a root, if not, the new node becomes the root.
b. If there is a root, check if the value of the new node is greater than or less than the value of the root.
c. If it is greater:
i. Check to see if there is a node to the right.
ii. If there is, move to that node and repeat these steps.
iii. If there is not, add that node as the right property.
d. If it is less:
i. Check to see if there is a node to the left.
ii. If there is, move to that node and repeat these steps.
iii. If there is not, add that node as the left property.
1. Create a new node.
2. Starting at the root:
a. Check if there is a root, if not, the new node becomes the root.
b. If there is a root, check if the value of the new node is greater than or less than the value of the root.
c. If it is greater:
i. Check to see if there is a node to the right.
ii. If there is, move to that node and repeat these steps.
iii. If there is not, add that node as the right property.
d. If it is less:
i. Check to see if there is a node to the left.
ii. If there is, move to that node and repeat these steps.
iii. If there is not, add that node as the left property.
1. Starting at the root:
a. Check if there is a root, if not, the tree is empty.
b. If there is a root, check if the value of the new node is greater than or less than the value of the root.
c. If it is greater:
i. Check to see if there is a node to the right.
ii. If there is, move to that node and repeat these steps.
iii. If there is not, the node does not exist in the tree.
d. If it is less:
i. Check to see if there is a node to the left.
ii. If there is, move to that node and repeat these steps.
iii. If there is not, the node does not exist in the tree.
1. Starting at the root:
a. Check if there is a root, if not, the tree is empty.
b. If there is a root, check if the value of the new node is greater than or less than the value of the root.
c. If it is greater:
i. Check to see if there is a node to the right.
ii. If there is, move to that node and repeat these steps.
iii. If there is not, the node does not exist in the tree.
d. If it is less:
i. Check to see if there is a node to the left.
ii. If there is, move to that node and repeat these steps.
iii. If there is not, the node does not exist in the tree.