Fast, efficient and easy-to-use JSON parser and serializer for Dart.
Crimson does not verify your JSON!
- 🏎️ Fast: Like really fast. Crimson parses JSON in a single pass.
- 🌻 Easy to use: Crimson is designed to be easy to learn and use.
- 💃 Flexible: Crimson can partially parse and serialize JSON.
- 🥶 Freezed support: Crimson supports freezed classes.
- 🪶 Lightweight: Crimson is lightweight and has no third-party dependencies.
After adding Crimson to your pubspec.yaml, you can start annotating your classes with @json and optionally @JsonField():
import 'package:crimson/crimson.dart';
part 'tweet.g.dart';
@json
class Tweet {
DateTime? createdAt;
String? tweet;
int? favoriteCount;
}Now you just need to run pub run build_runner build to generate the necessary code.
import 'package:crimson/crimson.dart';
void main() {
final jsonBytes = downloadTweets();
final crimson = Crimson(jsonBytes);
final tweets = crimson.readTweetList();
final writer = CrimsonWriter();
writer.writeTweetList(tweets);
final bytes = writer.toBytes();
}That's it! You can now parse and serialize JSON with ease.
Annotate properties with @jsonIgnore to ignore them:
@json
class Tweet {
DateTime? created_at;
String? tweet;
@jsonIgnore
int? favoriteCount;
}Use the @JsonName() annotation to rename individual fields:
@json
class Tweet {
@JsonName('created_at')
DateTime? createdAt;
@JsonName('text', aliases: {'alias1', 'alias2'})
String? tweet;
}The same works for enum values:
@json
enum TweetType {
tweet,
@JsonName('re-tweet')
retweet,
}If you want to rename all fields or enum values, you can use @jsonKebabCase and @jsonSnakeCase:
@jsonKebabCase
class Tweet {
DateTime? createdAt; // created-at
String? tweet; // tweet
int? favoriteCount; // favorite-count
}
@jsonSnakeCase
enum PlaceType {
country, // country
largeCity, // large_city
smallCity, // small_city
}Crimson supports generating a fromJson() constructor and a toJson() extension method for your classes use Uint8List.
Just add the following line to your class. The .toJson() method is generated using an extension.
@json
class Tweet {
// ...
factory Tweet.fromJson(Uint8List json) => _$TweetFromJson(json);
}Alternatively you can use fromBytes() and toBytes(). It's equivalent to fromJson() and toJson().
@json
class Tweet {
// ...
factory Tweet.fromBytes(Uint8List bytes) => _$TweetFromBytes(bytes);
}Crimson supports RFC 6901 JSON pointers to access nested JSON fields:
{
"user": {
"name": "Simon Choi"
},
"tweets": [
{
"text": "Hello World!"
},
{
"text": "Hello Crimson!"
}
]
}We can access the name field of the user object and the text field of the second tweet by providing a JSON pointer:
@json
class Tweet {
@JsonName('/user/name')
String? userName;
@JsonName('/tweets/1/text')
String? secondTweet;
}JSON pointers are evaluated at compile time and optimized code is generated so there is no runtime overhead.
Fields using JSON pointers are ignored for serialization.
Important: You can only use a pointer prefix once in a class. For example, you can't use /user and /user/name in the same class.
You can use custom JSON converters to convert between JSON and Dart types using the @JsonConvert() annotation:
@json
class Tweet {
String? tweet;
@JsonConvert(fromJson: jsonIntToBool, toJson: boolToJsonInt)
bool? isFavorite;
}
bool jsonIntToBool(int json) => json >= 1;
int boolToJsonInt(bool value) => value ? 1 : 0;Crimson supports classes annotated with @freezed from the freezed package.
import 'package:crimson/crimson.dart';
part 'tweet.g.dart';
part 'tweet.freezed.dart';
@freezed
class Tweet with _$Tweet {
@json
const factory Tweet({
DateTime? created_at,
@JsonField(name: 'text') String? tweet,
int? reply_count,
int? retweet_count,
int? favorite_count,
}) = _Tweet;
}The following benchmarks give you an idea about the JSON parsing performance of Crimson. The benchmarks were run on a MacBook with M1 Pro and 32 GB of RAM using Twitter API data.
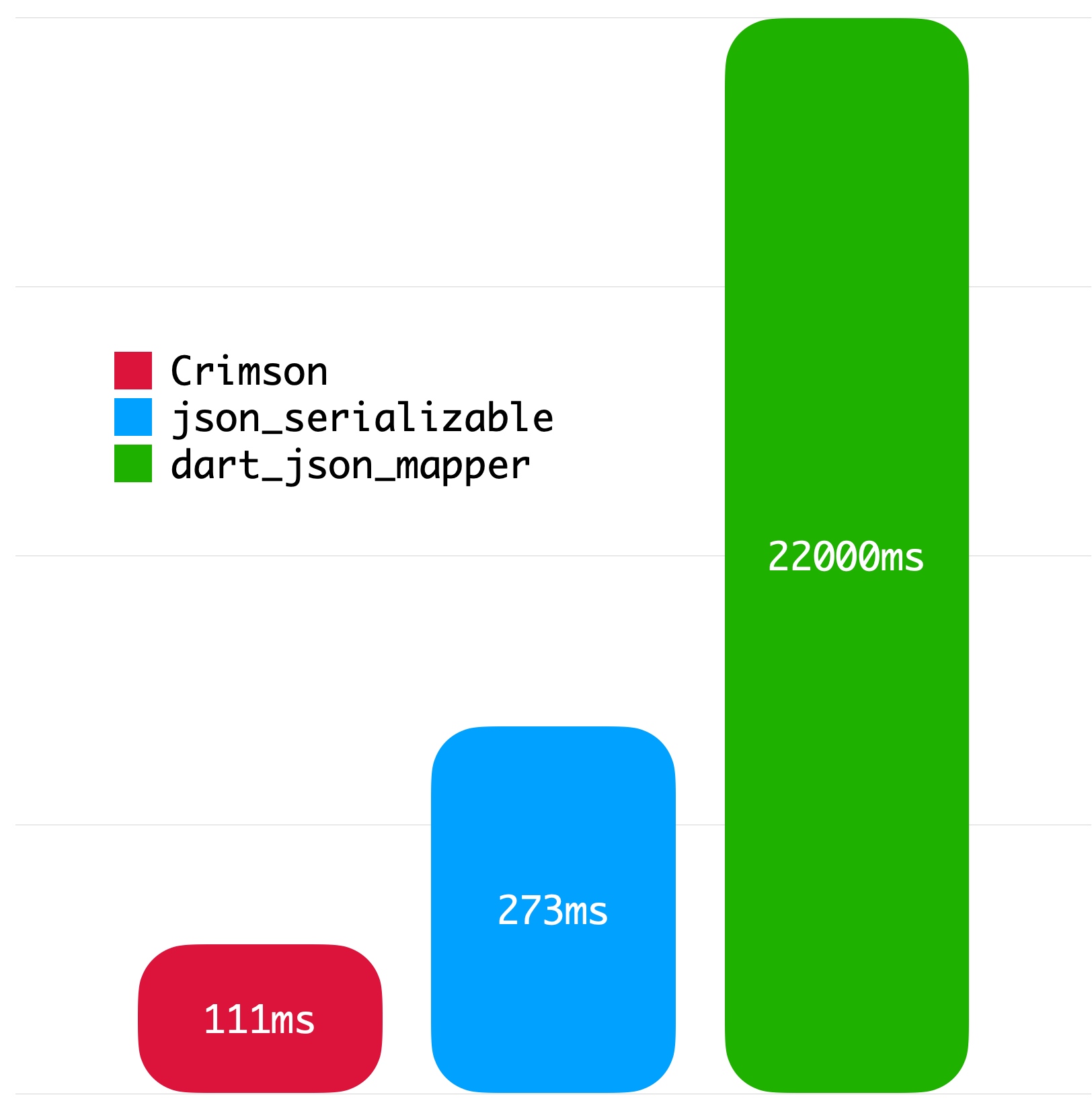
|
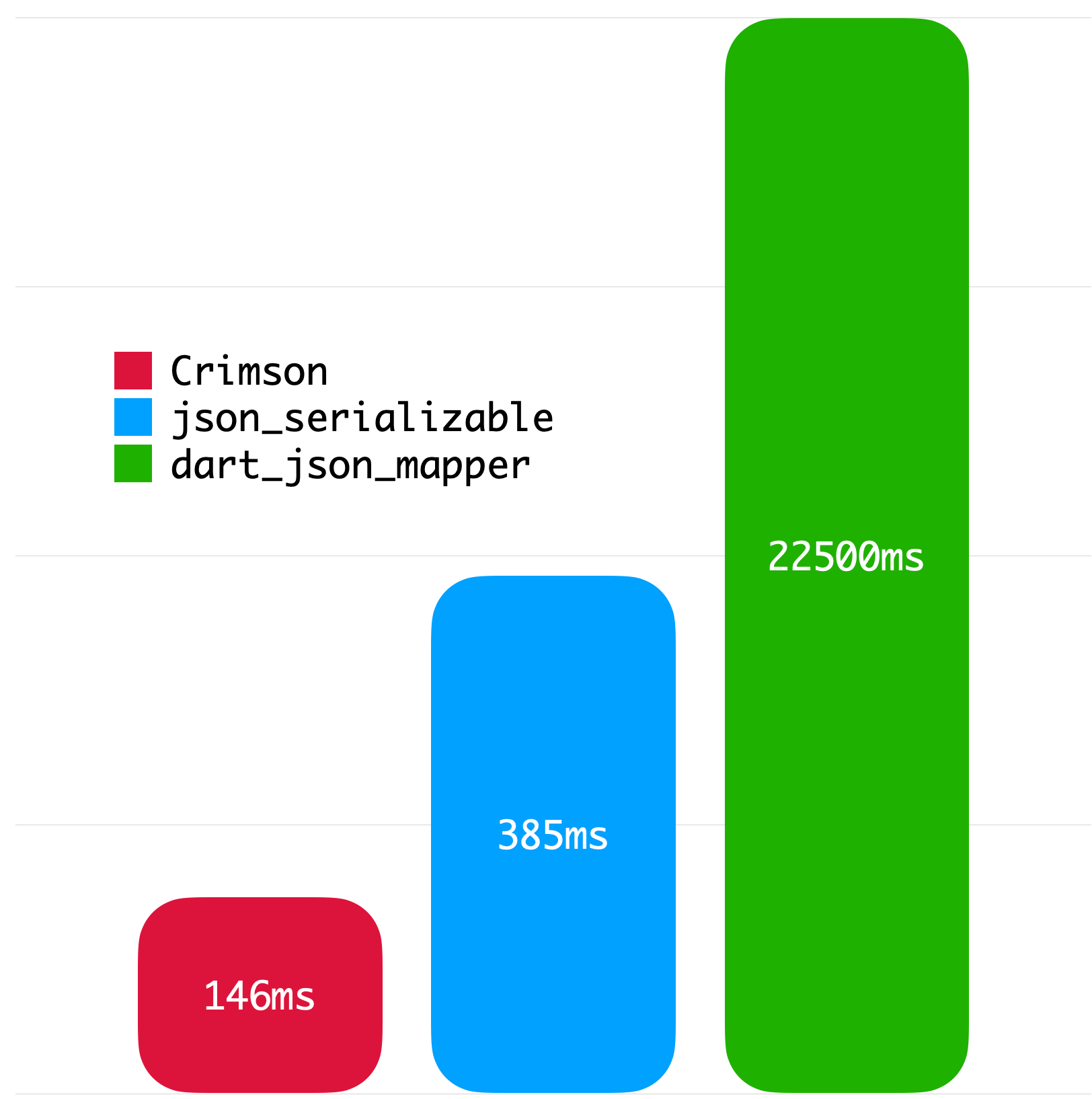
|
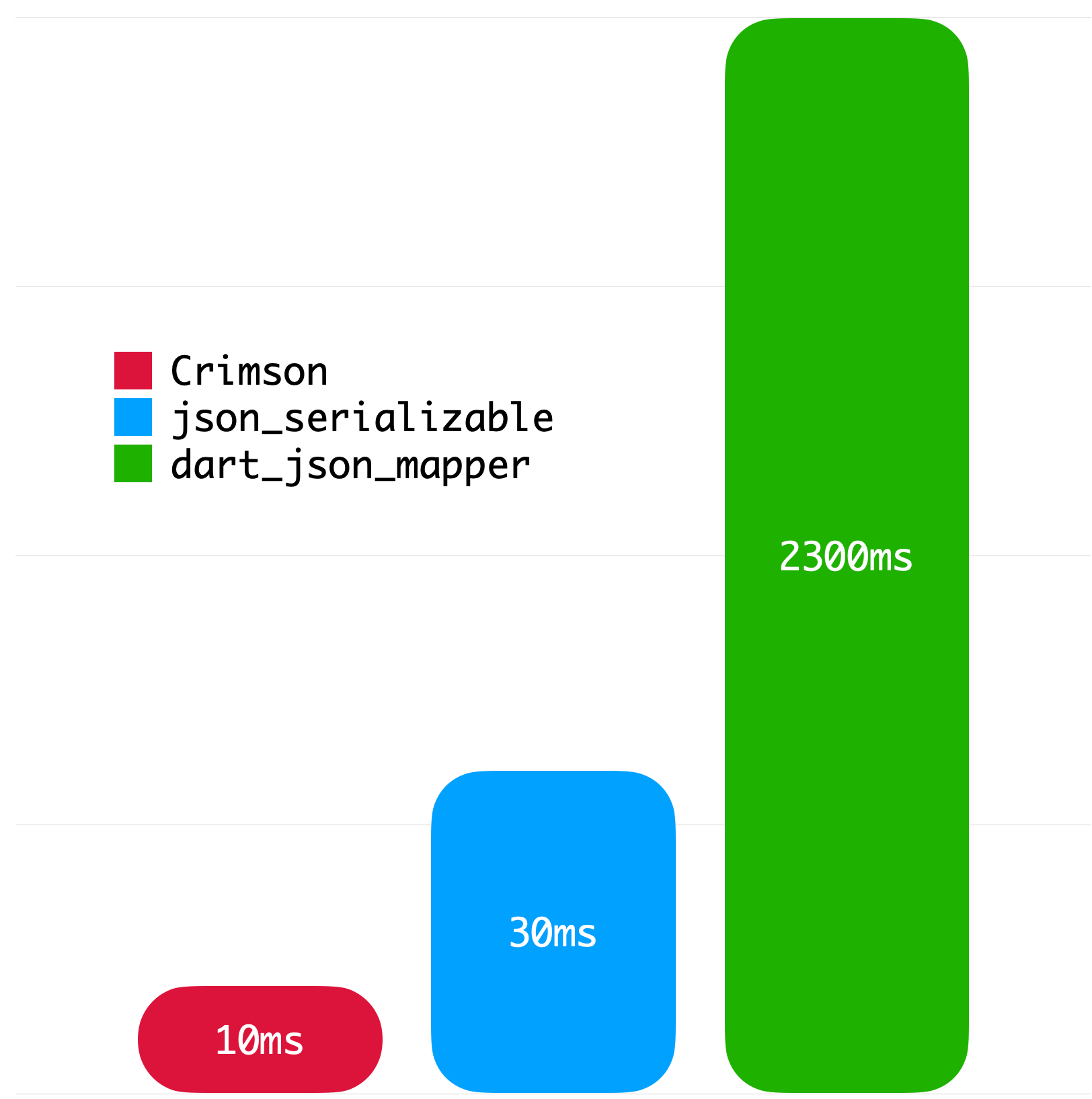
|
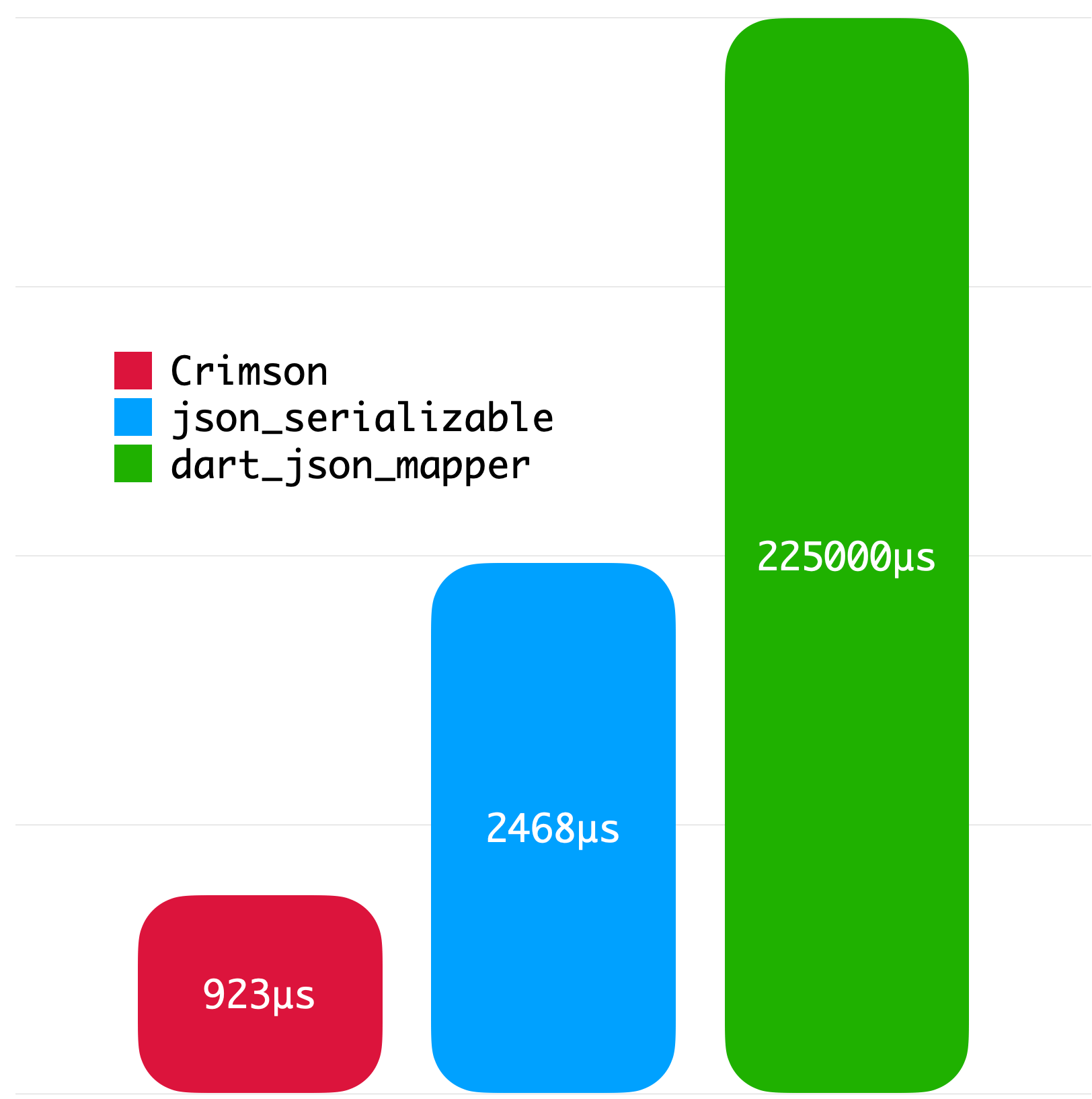
|
Copyright 2023 Simon Choi
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.



